Understanding LTE Signalling Radio Bearers: A Comprehensive Guide
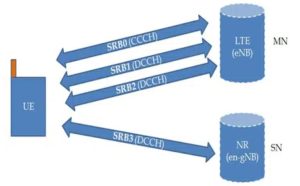
In the world of LTE (Long Term Evolution), signaling radio bearers (SRBs) play a crucial role in maintaining effective communication and connectivity. These SRBs, which include SRB0, SRB1, and SRB2, facilitate the transfer of necessary signaling messages between user equipment (UE) and network nodes such as eNodeB and MME. By understanding the functions and distinctions of these SRBs, one can appreciate their importance in ensuring seamless and reliable LTE communications.
What are LTE Signalling Radio Bearers?
Overview of Radio Bearers and Their Purpose
Radio bearers in LTE networks are essentially the conduits that carry data between the network and the end-user devices. These bearers help manage communication by establishing a dedicated path for the transfer of radio resource control (RRC) and non-access stratum (NAS) messages. This ensures that both control and user plane messages are effectively managed, providing clear instructions and reliable connections.
Role of SRB in LTE Network
Signalling Radio Bearers (SRBs) are specialized types of radio bearers designed to handle control messages in LTE networks. SRBs are utilized for the transmission of RRC signaling messages between UE and eNodeB. Additionally, NAS signaling messages, which travel between UE and MME, can also be encapsulated within RRC messages and then transferred using SRBs. Hence, SRBs play a pivotal role in maintaining the signaling backbone of LTE communications.
Key Types of LTE Signalling Radio Bearers
There are three essential types of SRBs in LTE: SRB0, SRB1, and SRB2. Each one serves a specific purpose and is configured based on network requirements. SRB0 is used primarily for initial RRC messages. SRB1 handles both RRC messages and NAS messages, while SRB2 is predominantly used for encapsulating NAS messages. SRB2 is typically configured after the activation of security protocols, ensuring that sensitive data is appropriately protected during transmission.
What Are the Differences Between SRB0, SRB1, and SRB2?
Distinguishing SRBs by RLC Modes
SRB0 utilizes the transparent mode of Radio Link Control (RLC), which means it does not perform any retransmission or error correction. Conversely, SRB1 and SRB2 use acknowledged mode RLC, which includes error correction and retransmission mechanisms. This ensures higher reliability and integrity for the transmitted control messages, making SRB1 and SRB2 more robust for critical signaling data.
SRB Usage Scenarios in LTE
Each SRB is employed in specific scenarios based on their unique functionalities. SRB0 is used for initial connection establishment, carrying initial RRC messages. SRB1 is used for ongoing RRC signaling and initial NAS message exchanges when SRB2 is not configured. SRB2, on the other hand, is dedicated to encapsulating NAS messages once robust security features are in place. This hierarchical usage ensures optimal performance and security within the LTE network.
Prioritization Among SRBs
In LTE signaling, prioritization among SRBs is essential to manage the criticality of messages effectively. SRB1 has a higher priority than SRB2 due to its role in handling both RRC and NAS messages. SRB2 is configured only after security activation and has a lower priority, ensuring security and integrity for NAS message encapsulation. This prioritization mechanism ensures that essential control messages are transmitted first, maintaining network stability and performance.
How Do LTE SRB0, SRB1, and SRB2 Work?
Understanding SRB0 for Initial RRC Messages
SRB0 is responsible for transferring initial RRC messages using the Common Control Channel (CCCH). These initial messages are crucial for setting up the communication link between UE and eNodeB. By operating in transparent mode RLC, SRB0 ensures quick and efficient initial signaling without added complexity of error correction, providing a fast setup of the connection.
Functions of SRB1 in LTE Signalling
SRB1 handles both ongoing RRC signaling and initial NAS messages using the Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH). It operates in acknowledged mode RLC, ensuring that errors are corrected and messages are accurately transferred. SRB1 forms the backbone for maintaining robust signaling paths post-initial connection, crucial for sustaining a reliable LTE communication link.
Role of SRB2 for NAS Encapsulation
SRB2 is primarily used for encapsulating NAS messages within RRC messages on the DCCH. This bearer is configured after security has been enabled on the network, ensuring that sensitive signaling data is transmitted securely. By using acknowledged mode RLC, SRB2 guarantees the integrity and reliability of NAS message transfer, catering to high-security requirements of LTE networks.
Why Are Radio Bearers Important in LTE?
Ensuring Reliable Data Transfer
Reliable data transfer in LTE is ensured by the effective management of SRBs. SRBs provide the necessary channels for control messages, ensuring that both RRC and NAS messages are accurately and efficiently transmitted. This reliability is fundamental to maintaining seamless LTE services, reducing latency, and preventing dropped connections.
Prioritization and Traffic Management
Effective prioritization and traffic management are achieved through the hierarchical arrangement of SRBs. By prioritizing SRB1 over SRB2 and configuring them based on security and function, LTE networks can manage critical signaling traffic efficiently. This traffic management enhances the overall quality of service and user experience, providing robust and responsive communication.
Security Implications of SRBs
Security in LTE networks is significantly bolstered by SRBs. SRB2’s configuration post-security activation ensures that NAS messages are encapsulated and transferred securely. The use of acknowledged mode RLC in SRBs guarantees data integrity and protection against transmission errors, safeguarding sensitive signaling information from potential vulnerabilities and breaches.
Conclusion
LTE Signalling Radio Bearers (SRBs) are integral to maintaining a cohesive and reliable LTE network. By efficiently managing the transfer of RRC and NAS signaling messages, SRBs like SRB0, SRB1, and SRB2 ensure that vital control information is securely and accurately transmitted. Understanding the distinct roles and operations of each SRB helps in appreciating their contribution to the seamless functioning of LTE communications.





